SHMFF Users Realize Record-High Electrostrain in Lead-Free Piezoceramics
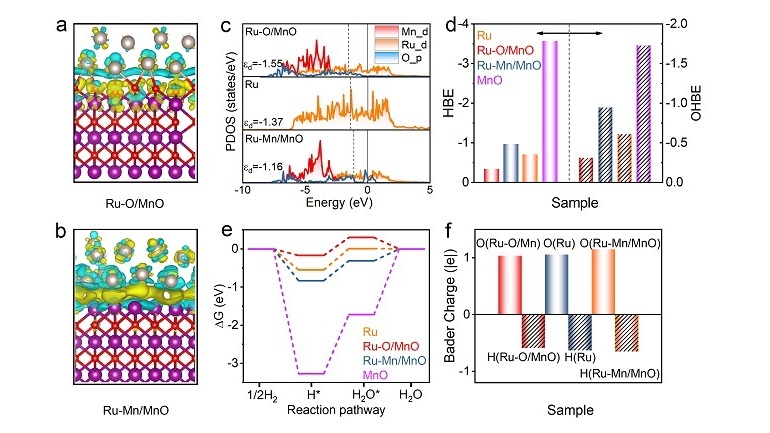
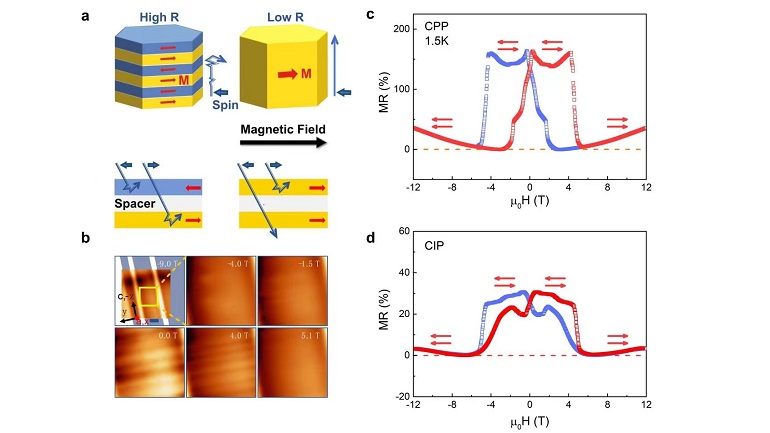
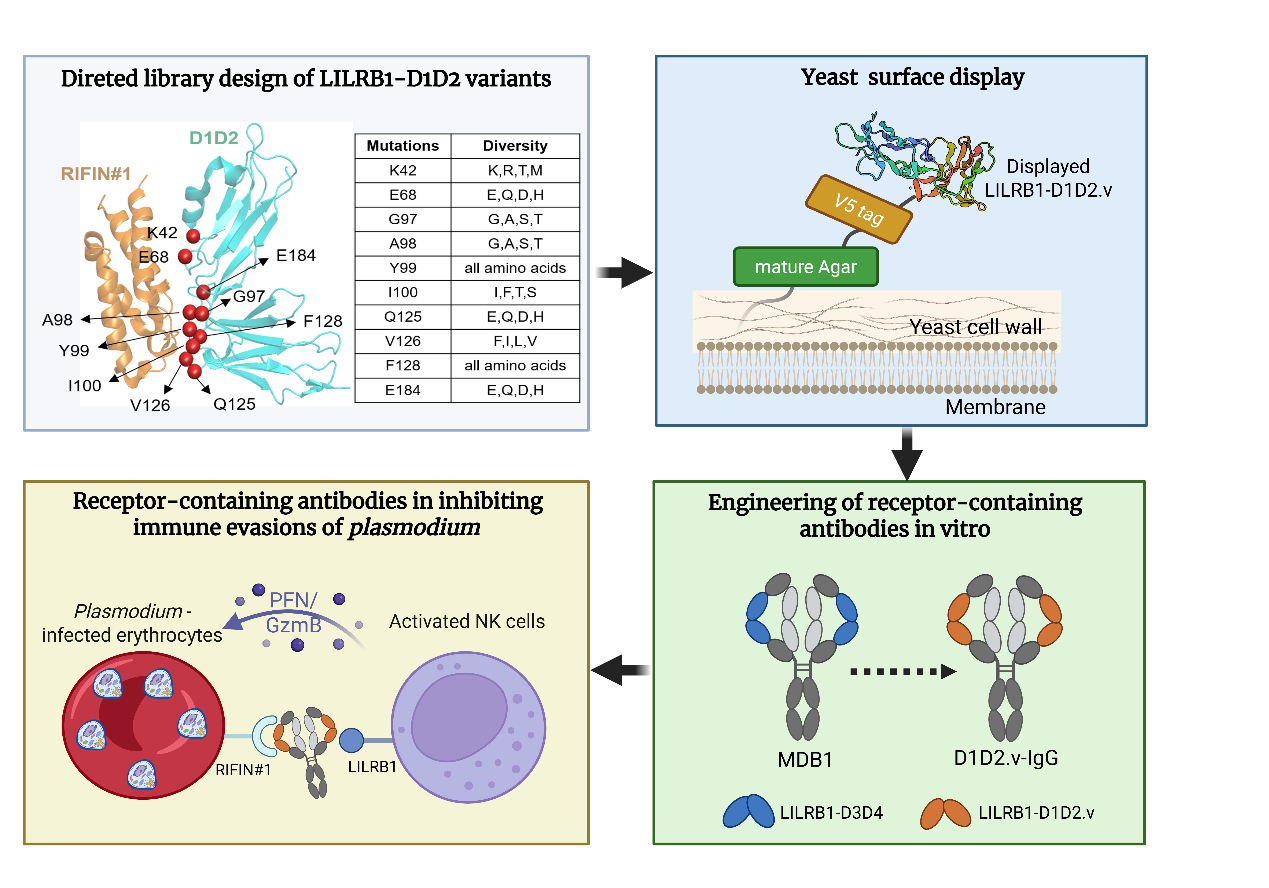
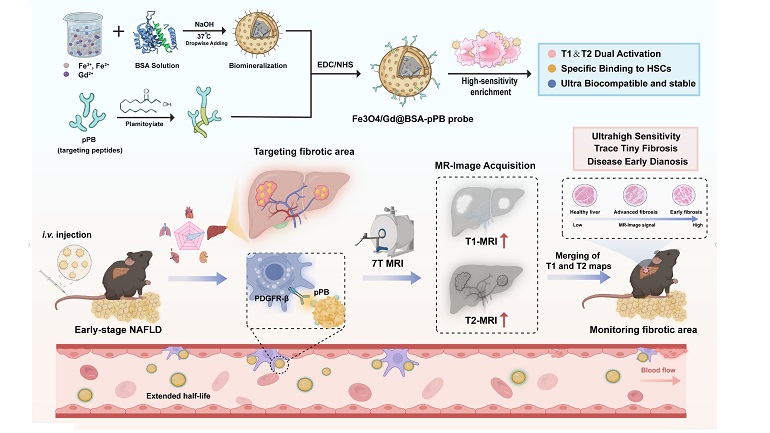
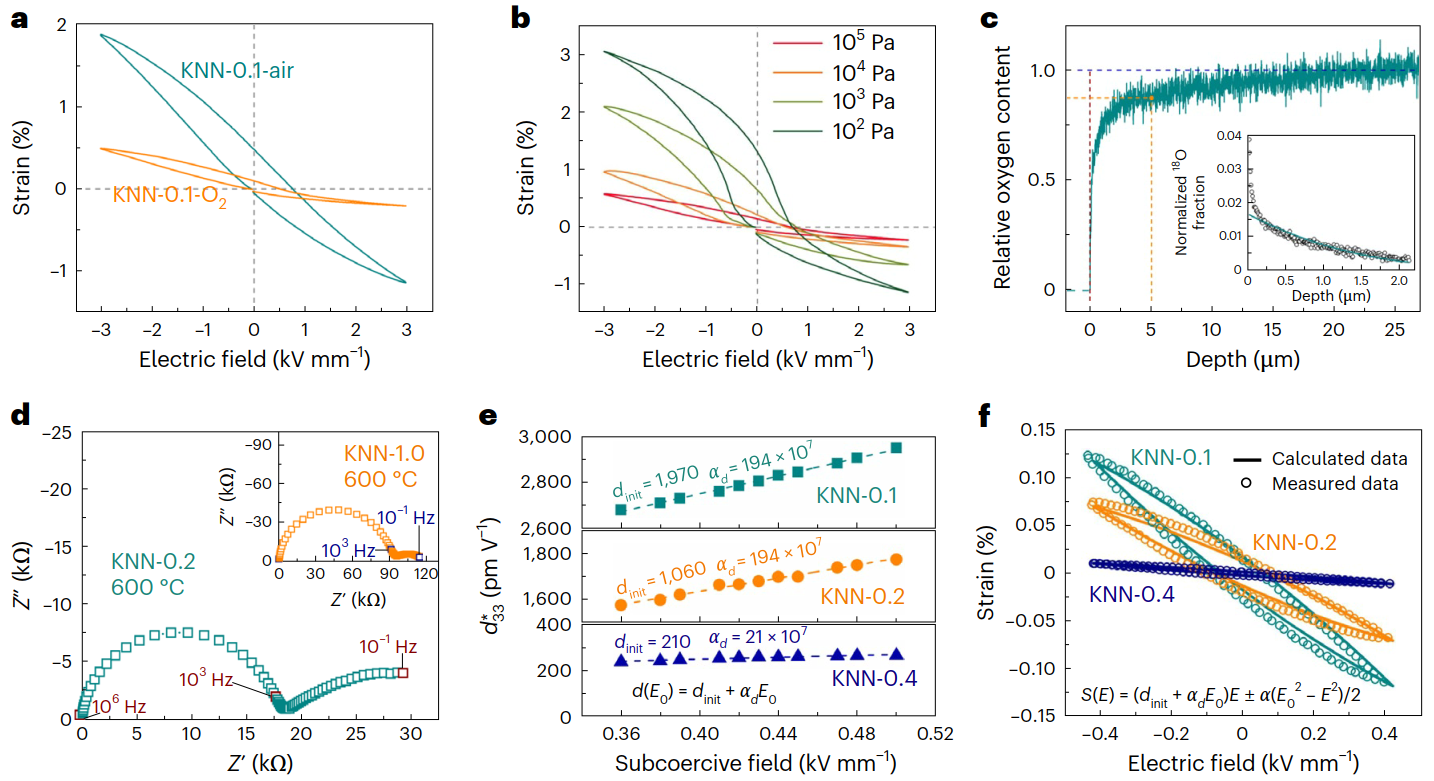
Taking advantage of the electron spin resonance (ESR) spectrometer at the Steady High Magnetic Field Experimental Facility (SHMFF), researchers from Tsinghua University, in collaboration with Beijing Institute of Technology, the University of Wollongong (Australia), and the Hefei Institutes of Physical Science of the Chinese Academy of Sciences, have achieved ultrahigh piezoelectric strain of 1.9% in (K,Na)NbO3 (KNN) lead-free piezoelectric ceramics.
Mar 06, 2025