
Recently, the research team from Shenguang Ⅱ Laser facility at the Shanghai Institute of Optics and Fine Mechanics (SIOM) of the Chinese Academy of Sciences has realized ultra-flat wavefront sensing and measurement based on photon sieve self-interference technology, addressing the challenge of interferometric measurement for weakly distorted wavefronts.
Related research findings were published in Optics and Lasers in Engineering under the title of "Micro-defocus photon-sieve radial-shearing interferometer for ultra-flat wavefront sensing."
Interferometry plays a crucial role in various wavefront measurement techniques, and high-precision interferometric methods have significantly advanced the development of different scientific disciplines. Different optical path structures exhibit varying resistance to external environmental disturbances. Compared to multi-path interference configurations, the common-path structure of self-interference offers greater robustness and strong anti-interference capability. The interference fringes generated by weakly distorted wavefronts exhibit extremely subtle changes, resulting in interference patterns with very low signal-to-noise ratios that are difficult to measure with high precision.
Building on their previous research on photon sieves, the research team introduced a spherical wave carrier frequency to the interference signal using cascaded photon sieves with micro-defocus. This approach causes the weakly distorted wavefront under test to produce strongly varying interference fringes at the recording position, which are then captured by a photodetector. Finally, the wavefront under test is reconstructed through interference pattern demodulation technology.
Figure 1 shows the experimental interference patterns captured at two different times (a, b, d, e), with the corresponding wavefront gradients shown in (c) and (f). Figure 2 (a, b) presents the reconstructed wavefronts under test from the two experiments, which are consistent with the measurement results from (c) ZYGO.
This research work received support from the National Natural Science Foundation of China and the Chinese Academy of Sciences Strategic Priority Research Program (Category A).
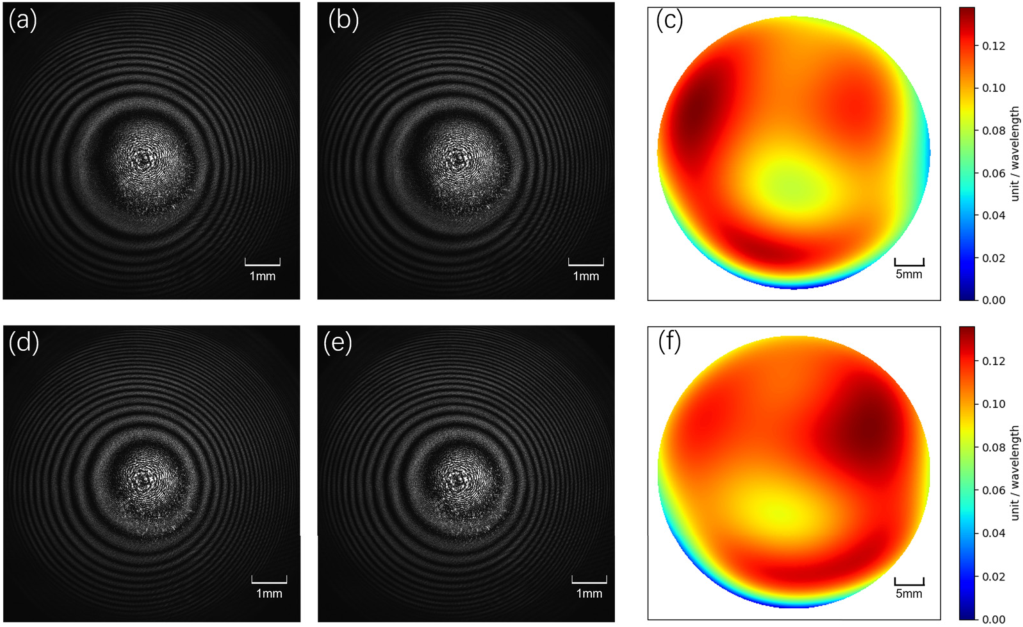
Fig. 1. Micro-defocus experimental process (a) and (b) Interferograms before and after placing the ultra-flat optical glass with a 1 mm defocus; (c) Differential phase difference extracted from (a) and (b); (d) and (e) Interferograms before and after placing the ultra-flat optical glass with a 2 mm defocus; (f) Differential phase difference extracted from (d) and (e).
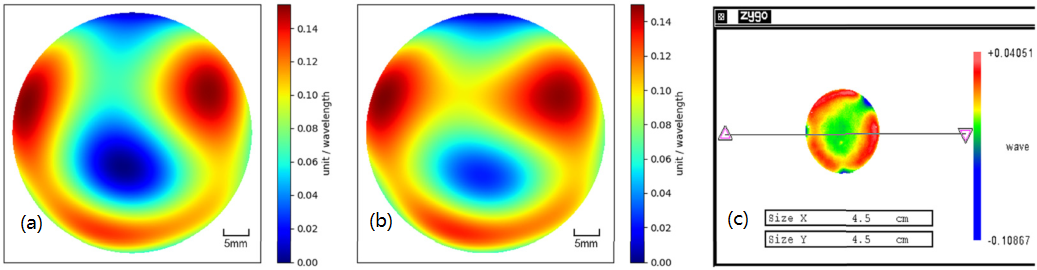
Fig. 2. Micro-defocus experimental results (a) Reconstruction result with 1 mm defocus; (b) Reconstruction result with 2 mm defocus; (c) Measurement result from the ZYGO interferometer.